elisa test optical density|elisa interpretation : purchase For patients who had more than one PF4 ELISA test performed, the confirmatory test result of the initial positive PF4 ELISA (OD ≥ 0.4) designated the patient as confirm+ or confirm-, and the maximal OD of the positive test results was utilized for data analysis. . Zwicker JI, Uhl L, Huang WY, et al. Thrombosis and ELISA optical density .
This combination of introducing cold water and pressurized air helps reduce the temperature of the liquid load quickly and safely.
{plog:ftitle_list}
The fundamental principles behind autoclave sterilization are pressure and temperature. Microorganisms have different heat resistance levels, and by subjecting them to high temperatures, their cellular structures break .
how to interpret elisa results
There are many ELISA tests for particular molecules that use the matching antibodies. ELISA tests are broken into several types of tests based on how the analytes and antibodies are bonded and used. The major types are described here. The steps of direct ELISA follows the mechanism below:This page details the recommended guidelines for calculating results from ELISA data and statical assay validation. Depending on the type of ELISA used (qualitative, semi-quantitative or quantitative) data output will vary. Therefore you should choose the specific ELISA you want to use based on the data that you want to analyse.Patients with MAC-ELISA and NS1Antigen non-reactive but GAC-ELISA reactive results (n =57) in their first test were followed up and repeated sampling was asked for IgG index values were calculated according to the manufacturer's instruction and classified as: low (2.2-2.5), medium (2.5-4.0) and high (>4.0).
In ELISA, the optical density measurement often gives low optical density (OD) readings; that's low or poor signals, and meanwhile, what shows in the 96-well plate is insufficient color development. This section is intended to recommend possible causes and relative troubleshooting for the problem of ELISA insufficient color development.
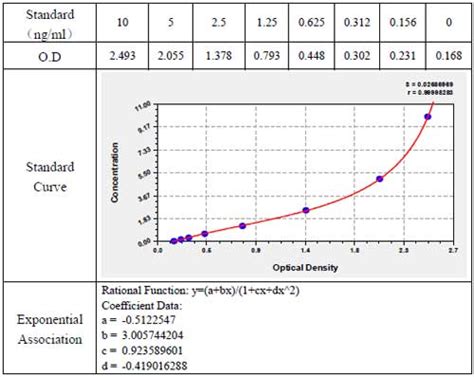
ELISA data is typically graphed with optical density vs log concentration to produce a sigmoidal curve as shown in Figure 6. Known concentrations of antigen are used to produce a standard curve and then this data is used to measure the concentration of unknown samples by comparison to the linear portion of the standard curve.
For patients who had more than one PF4 ELISA test performed, the confirmatory test result of the initial positive PF4 ELISA (OD ≥ 0.4) designated the patient as confirm+ or confirm-, and the maximal OD of the positive test results was utilized for data analysis. . Zwicker JI, Uhl L, Huang WY, et al. Thrombosis and ELISA optical density .The ELISA is a rapid test used for detecting and quantifying antibodies or antigens against viruses, bacteria, and other materials. . bound enzyme, and the optical density is read with an ELISA plate reader. Note: The steps and reagents used can vary in an ELISA. Refer to the product insert for specific information. Clinical and laboratory characteristics associated with a high optical density anti-platelet factor 4 ELISA test J Blood Med. 2015 Nov 19:6:277-83. doi : 10.2147 . Associations between OD and 18 clinical characteristics were calculated using the Fisher's exact test for categorical variables and Wilcoxon rank-sum test for continuous variables. .
All patients who underwent ELISA testing were eligible for inclusion (n = 496). Irrespective of the results, all subjects had confirmatory testing with a serotonin release assay (SRA). We compared a threshold optical density (OD) > 1.00 to the current definition of a positive ELISA (OD > 0.40) as a screening test for a positive SRA.
Higher ELISA optical density (OD) measurements correlated significantly with thrombosis (1.41 ± 0.87 vs. 0.79 ± 0.46, P < 0.001). Patients with . Decision analysis for use of platelet aggregation test, carbon 14‐serotonin release assay, and heparin‐platelet factor 4 enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of heparin‐induced . How to Analyze ELISA: 1. Run samples in duplicates or triplicates to ensure statistical accuracy. Average the readings for each standard, control, and sample, and subtract the average zero standard optical density (O.D.). This experiment setup helps identify patterns and trends by reducing variability. 2. Create a standard curve by plotting the average .
The signal is quantified by measuring the optical density in a photometer at the appropriate wavelength [1]. The ELISA replaces the radioimmunoassay applied for a long time, in which radioactive material is used for detection [3]. A brief overview of the different ELISA methods is given below. Overview of different ELISA methods.The antibody was labeled by enzyme. After the substrate of the enzyme was added, the substrate becomes a colored product under catalysis of the enzyme-catalyzed, which is directly related to the amount of test substance. The optical density of the reaction product is typically proportional to the amount of analyte being measured. In addition to SRA, an ELISA immunoassay can be used to detect anti-PF4/heparin antibodies in the patient’s serum. The results are expressed in terms of optical density (OD), which corresponds to the antibody’s concentration. The positive threshold of this test in most commercially available kits is usually in the vicinity of an OD of 0.4 .The first polyspecific ELISA to detect HIT antibodies was developed in 1992. 21, 32, 45 In this test, suspected patients’ serum/plasma is added to PF4–polyanion complex–embedded microtiter plate wells. The semiquantitative nature of the test allows assessment of intensity of color change, and measures it as optical density (OD) at a .
Sera with low ELISA optical density (OD) values (0.4–1) activated on average 5.6, sera with intermediate ELISA OD values (>1–2.5) activated on average 7.3, and sera with high ELISA OD values (>2.5) activated on average 8.6 out of 10 panel platelets. . For all samples that test positive with ELISA, a functional flow cytometric test is .on a specific substrate (e.g., ABTS, SuperAqua Blue or TMB). The optical density of the end-product is measured using a spectrophotometer. eBioscience offers a variety of ELISA to cytokines, chemokines, growth factors and protein released upon cell death. General Notes A.
how to analyze elisa data
In addition to SRA, an ELISA immunoassay can be used to detect anti-PF4/heparin antibodies in the patient’s serum. The results are expressed in terms of optical density (OD), which corresponds to the antibody’s concentration. The positive threshold of this test in most commercially available kits is usually in the vicinity of an OD of 0.4 .Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like The ELISA was the first screening test widely used for HIV because of its high sensitivity. In an ELISA, a person's serum is diluted 400-fold and applied to a plate to which HIV antigens are attached. . Numbers are expressed as optical density at 450 nm. The cutoff value .Correlation of ELISA Optical Density With Clinical Diagnosis of Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia: A Retrospective Study of 104 Patients With Positive . calculated using the unpaired t test. A linear regression curve was performed using the values of OD and ‘‘4T score.’’ A receiver–operator curve (ROC) between OD and clinical .We investigated the usefulness of clinical scores and heparin/PF4 ELISA optical density (OD) as a diagnostic marker and thrombosis predictor in HIT. Methods: We analyzed 92 patients with suspected HIT. The heparin/PF4 antibody was measured using a commercial ELISA kit (GTI, USA). For each patient, the 4 T's score and Chong's score were calculated.
The optical density (OD) of three negative control sera was determined at serum dilutions of 1:100 to 1:512,000. E.g., for the dilution of 1:100: negative control 1 = 0.011, negative control 2 = 0 .
ELISA test results, what does a positive ELISA test tell you? ELISA results may be interpreted quantitatively, qualitatively or semi-quantitatively. In a quantitative assay, a serial dilution of a known standard is used to enable the generation of a standard curve, normally of optical density (OD) versus concentration. From this, the precise .In ELISA, the optical density measurement often gives low optical density (OD) readings; that's low or poor signals, and meanwhile, what shows in the 96-well plate is insufficient color development. This section is intended to recommend possible causes and relative troubleshooting for the problem of ELISA insufficient color development. Its diagnosis is primarily clinical but can be supported by several laboratory tests. ELISA for anti-PF4/heparin antibodies, which is the most widely-available technique, is expressed in terms of optical density (OD) results. This test was shown to have good sensitivity but poor positive predictive value.The concentration of antigen in a sample can then be calculated using the optical density (OD). Figure 2. A typical standard curve. Shown is a standard curve for an IFN-γ ELISA. To work out the concentration of antigen in a sample, a standard curve using a solution of known concentration needs to be prepared.
The sensitivity of each ELISA test at different optical density (OD) cut-points was plotted vs. the specificity to generate receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curves . The herdacc program was used to identify the number of seropositive pigs per farm, which resulted in the optimal herd sensitivity and specificity . These numbers were used .where y i is the ith measured optical density (OD) or absorbance, x i is MC concentration, and α 1, ., α 4 are model parameters to be estimated. The parameters α 1 and α 4 define the high and low bounds of OD respectively, α 3 is the MC concentration value at which OD is at the middle of the range ((α 1 + α 4)/2), and α 2 defines the shape of the curve.
Dissolve 1.7 g yeast nitrogen base (w/o ammonium sulfate and w/o amino acids) and 5 g of (NH 4) 2SO 4 in 100 ml of distilled water, filter sterilize and transfer sterilely to a sterile bottle or to .
elisa test optical density|elisa interpretation